Prepare to soar with the majestic hawks as we delve into the captivating realm of their extraordinary flight capabilities. The hawk can soar answers lie within the intricate tapestry of their physical adaptations, environmental influences, and diverse hunting strategies. Join us on this breathtaking journey to unravel the secrets of these avian masters.
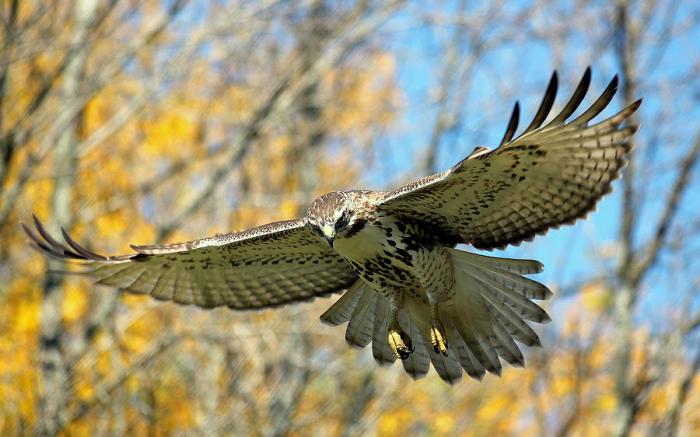
With their exceptional wingspan and aerodynamic design, hawks possess an unparalleled ability to glide effortlessly through the skies. Their soaring prowess grants them a distinct advantage in hunting, territorial defense, and attracting mates.
Characteristics of the Hawk’s Soaring Ability: The Hawk Can Soar Answers

Hawks are renowned for their exceptional soaring capabilities, allowing them to glide effortlessly through the skies with minimal effort. This remarkable ability is attributed to a combination of physical adaptations and refined techniques.
Physical Adaptations
Hawks possess several physical adaptations that enhance their soaring prowess. Their wings are long and broad, providing a large surface area for generating lift. The shape of the wings, with a slightly arched upper surface and a flat lower surface, creates an airfoil effect, which allows air to flow smoothly over the wings, generating lift while minimizing drag.
Additionally, hawks have lightweight bodies, reducing the energy required for sustained flight.
Wing Shape and Size, The hawk can soar answers
The shape and size of a hawk’s wings play a crucial role in soaring. The long, broad wings provide ample surface area for generating lift, enabling the hawk to stay aloft with minimal effort. The arched upper surface and flat lower surface of the wings create an airfoil effect, which allows air to flow smoothly over the wings, generating lift while minimizing drag.
This efficient aerodynamic design allows hawks to glide effortlessly through the air, covering long distances with minimal energy expenditure.
Soaring Techniques
Hawks employ various techniques to gain and maintain altitude while soaring. They utilize updrafts, rising columns of air, to gain altitude without expending energy. By circling within these updrafts, hawks can ascend to significant heights. Additionally, hawks use the technique of “dynamic soaring” to gain altitude by flying against the wind and using the wind’s energy to climb higher.
This technique requires precise control and coordination, but it allows hawks to soar for extended periods without losing altitude.
Environmental Factors Influencing Soaring
Environmental factors play a crucial role in a hawk’s ability to soar effortlessly through the skies. Understanding these factors provides insights into the remarkable soaring capabilities of these majestic birds.
Wind Speed and Direction
Wind is a fundamental factor that influences soaring. Hawks utilize strong winds to gain altitude and sustain their flight. Headwinds, which oppose the hawk’s forward motion, create lift and allow the hawk to climb higher. Tailwinds, on the other hand, assist the hawk’s forward movement, enabling it to cover greater distances.
Thermal Updrafts and Thermals
Thermal updrafts are columns of warm air rising from the ground. As hawks encounter these updrafts, they circle within them, gaining altitude without flapping their wings. Thermals, which are large areas of rising air, provide ideal conditions for soaring. Hawks can soar for hours within thermals, utilizing the rising air currents to conserve energy.
Weather Conditions
Weather conditions can significantly impact soaring. Rain, fog, and strong winds can hinder a hawk’s ability to soar. Rain can weigh down the hawk’s feathers, affecting its aerodynamics. Fog can reduce visibility, making it difficult for the hawk to locate thermals.
Strong winds can disrupt updrafts and make soaring challenging.
Soaring in Different Hawk Species

Soaring is a remarkable behavior exhibited by various hawk species, allowing them to effortlessly glide through the skies. These majestic birds possess unique adaptations and flight strategies that enable them to soar gracefully.
Among the soaring hawks, the Red-tailed Hawk is renowned for its exceptional soaring abilities. Its broad, rounded wings provide ample lift, while its forked tail enhances maneuverability. The Swainson’s Hawk, known for its long, narrow wings, excels in soaring over vast open areas.
To soar like a hawk, you need the right answers. The Hawk Can Soar Answers provides the guidance you need to excel in your studies. For further academic support, you may also find the Saxon Math Course 2 PDF helpful.
With these resources, you’ll be soaring high in no time, just like the mighty hawk.
Habitat and Prey Availability
Habitat and prey availability play a significant role in shaping the soaring behavior of hawks. Species that inhabit open landscapes, such as grasslands or prairies, have evolved to rely heavily on soaring to cover large distances in search of prey.
For instance, the Ferruginous Hawk, found in the western United States, utilizes soaring to locate and capture small rodents in its arid environment.
In contrast, hawks that dwell in forested areas may exhibit less frequent soaring behavior. The dense canopy limits their visibility and maneuverability, making it more efficient to perch and wait for prey to emerge.
Conservation and Management of Soaring Habitats

Protecting soaring habitats for hawks is crucial to ensure their survival and well-being. These habitats provide hawks with essential resources for hunting, nesting, and roosting. Threats to soaring habitats include urbanization, deforestation, and climate change.
Conservation Measures
Conservation measures to protect soaring habitats include:
- Establishing protected areas and conservation easements.
- Implementing sustainable forestry practices that minimize deforestation.
- Reducing the use of pesticides and other chemicals that can harm hawks.
li>Educating the public about the importance of soaring habitats and the need for their conservation.
Successful Conservation Efforts
Successful conservation efforts have been implemented in various regions to preserve soaring habitats for hawks. For instance, in the United States, the Golden Eagle National Conservation Area was established to protect critical habitat for golden eagles. Additionally, the Hawk Mountain Sanctuary in Pennsylvania has played a significant role in protecting migratory hawk populations by reducing illegal hunting and habitat destruction.
Clarifying Questions
How do hawks soar without flapping their wings?
Hawks utilize updrafts and thermals to gain altitude, allowing them to soar effortlessly for extended periods without expending excessive energy.
What are the benefits of soaring for hawks?
Soaring provides hawks with an advantage in hunting, enabling them to spot prey from great heights and conserve energy during long flights.
How do different hawk species vary in their soaring abilities?
Hawk species exhibit varying degrees of soaring capabilities, influenced by their habitat, prey availability, and wingspan.