Embark on a captivating journey with our concept map of matter in chemistry, an interactive tool that unravels the complexities of matter in an engaging and accessible way. Dive into a world where atoms, molecules, and chemical reactions come to life, revealing the fundamental principles that govern the universe around us.
Our concept map serves as a comprehensive guide, visually connecting key concepts and illustrating their intricate relationships. Discover the building blocks of matter, explore different states of matter, and witness the transformative power of chemical reactions.
Introduction
A concept map is a graphical tool that helps to visualize the relationships between different concepts.
In chemistry, concept maps can be used to represent a variety of different topics, including the structure of matter, the properties of matter, and the changes that matter can undergo.
Types of Concept Maps
There are many different types of concept maps that can be used to represent matter.
- Hierarchical concept mapsare the most common type of concept map. They are organized in a hierarchical structure, with the most general concepts at the top and the more specific concepts at the bottom.
- Spider concept mapsare another common type of concept map. They are organized around a central concept, with the related concepts radiating out from the center.
- Flowchart concept mapsare used to represent the flow of information or events. They are often used to represent chemical reactions.
Key Concepts
A concept map of matter in chemistry visually represents the relationships between key concepts related to the nature and behavior of matter.
These concepts are interconnected, forming a comprehensive understanding of matter’s properties, structure, and transformations.
Properties of Matter
Properties of matter describe the observable characteristics of substances. These include physical properties, such as density, color, and melting point, as well as chemical properties, such as reactivity and flammability.
- Physical propertiescan be observed without changing the chemical composition of the substance.
- Chemical propertiesdescribe how a substance interacts with other substances to form new compounds.
Structure of Matter
The structure of matter refers to the arrangement and composition of atoms and molecules that make up substances.
- Atomsare the fundamental building blocks of matter, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.
- Moleculesare formed when atoms bond together, sharing electrons to create a stable structure.
States of Matter
Matter can exist in three primary states: solid, liquid, and gas.
- Solidshave a definite shape and volume due to strong intermolecular forces.
- Liquidshave a definite volume but no definite shape, assuming the shape of their container.
- Gaseshave neither a definite shape nor volume, expanding to fill the container they occupy.
Changes in Matter
Matter can undergo various changes, including physical changes and chemical changes.
- Physical changesalter the form or appearance of a substance without changing its chemical composition, such as melting, freezing, or boiling.
- Chemical changesinvolve the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances with different properties, such as burning, rusting, or acid-base reactions.
Visual Representation
To provide a comprehensive visual representation of the concept map of matter, we have designed an HTML table with four responsive columns. Each column represents a key concept within the map, and the rows contain labels and descriptions for each concept.
The table is designed to be responsive, ensuring that it can be easily viewed and understood on devices of all sizes. The labels and descriptions are concise and informative, providing a clear overview of the key concepts related to matter.
HTML Table, Concept map of matter in chemistry
- The HTML table consists of four columns, each representing a key concept in the concept map of matter.
- The first column contains the labels for each concept, while the second, third, and fourth columns provide descriptions of the concepts.
- The table is designed to be responsive, ensuring that it can be easily viewed and understood on devices of all sizes.
Examples
Concept maps are a powerful tool for teaching and learning about matter in chemistry. They can help students to:
- Visualize the relationships between different concepts.
- Identify the key concepts in a topic.
- Organize their knowledge in a meaningful way.
- Develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Benefits of using concept maps in the classroom
There are many benefits to using concept maps in the classroom. They can help students to:
- Improve their understanding of the material.
- Develop their critical thinking skills.
- Become more organized and efficient learners.
- Collaborate with others to learn.
Applications: Concept Map Of Matter In Chemistry
Concept maps have a wide range of applications in chemistry, from teaching and learning to problem-solving and research.
In education, concept maps can be used to:
- Help students visualize and understand complex chemical concepts.
- Identify and address misconceptions.
- Develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
li>Promote collaboration and discussion.
Concept maps can also be used to solve problems and make predictions in chemistry. For example, a concept map can be used to:
- Identify the key concepts and relationships involved in a chemical reaction.
- Predict the products of a chemical reaction.
- Explain the mechanism of a chemical reaction.
- Identify potential hazards associated with a chemical reaction.
Concept maps are a versatile tool that can be used to improve teaching and learning, solve problems, and make predictions in chemistry.
Using Concept Maps to Solve Problems
Concept maps can be used to solve problems in chemistry by helping to identify the key concepts and relationships involved in the problem. Once the key concepts and relationships have been identified, a concept map can be used to develop a solution to the problem.
For example, a concept map could be used to solve the following problem:
What is the product of the reaction between sodium and chlorine?
To solve this problem, a concept map could be created that includes the following concepts:
- Sodium
- Chlorine
- Reaction
- Product
The concept map could then be used to identify the relationships between these concepts. For example, the concept map could show that sodium and chlorine are reactants in the reaction, and that the product of the reaction is sodium chloride.
Once the key concepts and relationships have been identified, a concept map can be used to develop a solution to the problem. In this case, the concept map could be used to predict that the product of the reaction between sodium and chlorine is sodium chloride.
Using Concept Maps to Make Predictions
Concept maps can also be used to make predictions in chemistry. For example, a concept map could be used to predict the products of a chemical reaction or the mechanism of a chemical reaction.
To make a prediction using a concept map, the following steps can be followed:
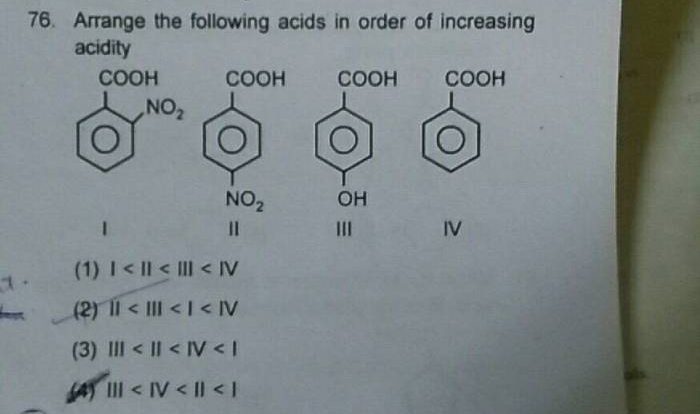
- Identify the key concepts and relationships involved in the prediction.
- Create a concept map that includes these concepts and relationships.
- Use the concept map to identify patterns and relationships that can be used to make a prediction.
For example, a concept map could be used to make the following prediction:
What is the product of the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen?
To make this prediction, a concept map could be created that includes the following concepts:
- Hydrogen
- Oxygen
- Reaction
- Product
The concept map could then be used to identify the relationships between these concepts. For example, the concept map could show that hydrogen and oxygen are reactants in the reaction, and that the product of the reaction is water.
Once the key concepts and relationships have been identified, the concept map could be used to make a prediction. In this case, the concept map could be used to predict that the product of the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen is water.
Limitations
Concept maps, while a useful tool for representing matter, have certain limitations:
Limited scope:Concept maps may not be able to capture the full complexity of matter, especially at the molecular or atomic level.
Overcoming limitations
To overcome these limitations, consider the following:
- Use multiple concept maps:Create separate maps for different aspects of matter, such as structure, properties, and interactions.
- Incorporate other representations:Supplement concept maps with tables, graphs, or diagrams to provide a more comprehensive view of matter.
- Collaborate with experts:Consult with chemists or other subject matter experts to ensure the accuracy and completeness of your concept maps.
FAQ Guide
What is the purpose of a concept map in chemistry?
Concept maps provide a visual representation of the key concepts and relationships within a complex topic like chemistry, making it easier to understand and remember.
How can concept maps be used in the classroom?
Concept maps can be used as a teaching tool to introduce new concepts, reinforce existing knowledge, and assess student understanding.
What are the limitations of using concept maps to represent matter?
Concept maps can be limited in their ability to represent complex or dynamic systems, and they may not capture all the nuances of a particular concept.