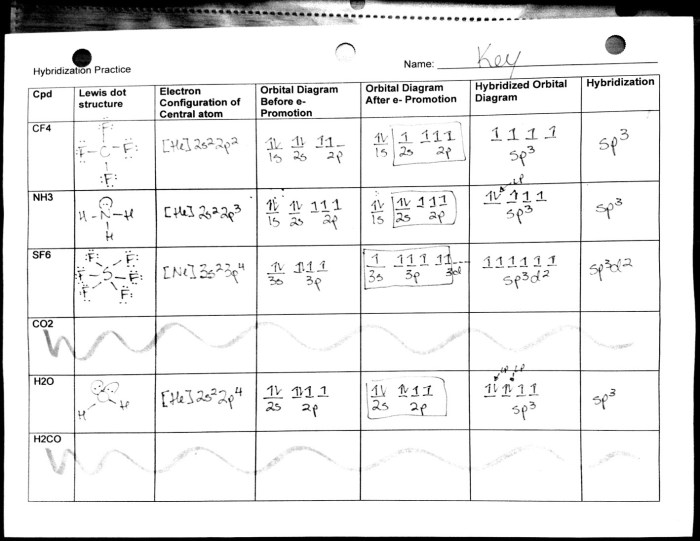
The molecular geometry POGIL answer key serves as a valuable resource for students seeking to master the fundamentals of molecular geometry. This comprehensive guide provides detailed explanations, engaging examples, and thought-provoking exercises that empower learners to grasp the intricacies of molecular structure and its profound implications in various scientific disciplines.
Delving into the principles of VSEPR theory, this answer key illuminates how electron-pair repulsion shapes molecular geometry. It explores the diverse types of molecular geometries, including linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral, and elucidates their influence on physical properties such as polarity, boiling point, and solubility.
1. VSEPR Theory
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory predicts the molecular geometry of molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom.
According to VSEPR theory, electron pairs arrange themselves in a way that minimizes the repulsion between them. This arrangement determines the molecular geometry, which can be linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, octahedral, etc.
Limitations of VSEPR Theory
- VSEPR theory does not consider the effects of bond length and bond strength.
- VSEPR theory cannot predict the molecular geometry of molecules with delocalized electrons.
2. Molecular Geometry and Properties
Types of Molecular Geometries
- Linear
- Trigonal planar
- Tetrahedral
- Octahedral
Influence of Molecular Geometry on Physical Properties
- Polarity
- Boiling point
- Solubility
3. Molecular Orbital Theory: Molecular Geometry Pogil Answer Key
Molecular orbital theory explains the electronic structure of molecules by describing the distribution of electrons in molecular orbitals. Molecular orbitals are formed by the combination of atomic orbitals.
The shape and energy of molecular orbitals determine the molecular geometry and the properties of the molecule.
Relationship between Molecular Orbital Theory and VSEPR Theory
VSEPR theory and molecular orbital theory are complementary models that can be used to predict the molecular geometry of molecules.
VSEPR theory provides a qualitative understanding of molecular geometry, while molecular orbital theory provides a more quantitative description.
4. Applications of Molecular Geometry
- Chemistry
- Biology
- Materials science
Importance of Molecular Geometry in Various Fields
Understanding molecular geometry is crucial for understanding the properties and reactivity of molecules.
Molecular geometry can be used to predict and explain chemical reactions, design new materials, and develop new technologies.
5. Experimental Determination of Molecular Geometry
X-ray Diffraction, Molecular geometry pogil answer key
X-ray diffraction is a technique that uses X-rays to determine the molecular structure of crystals.
X-rays are scattered by the electrons in the molecule, and the scattering pattern can be used to determine the positions of the atoms in the molecule.
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is a technique that uses the interaction of light with molecules to determine their molecular structure.
Different types of spectroscopy can provide information about the molecular geometry, including infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
Question & Answer Hub
What is VSEPR theory?
VSEPR theory (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) predicts the molecular geometry of a molecule based on the repulsion between electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom.
How does molecular geometry affect physical properties?
Molecular geometry influences physical properties such as polarity, boiling point, and solubility. For example, polar molecules have higher boiling points than nonpolar molecules due to stronger intermolecular forces.
What is the relationship between molecular orbital theory and VSEPR theory?
Molecular orbital theory provides a more detailed explanation of molecular geometry than VSEPR theory. It describes how electrons occupy molecular orbitals, which are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals, and how these orbitals influence molecular geometry.