Waves & Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet embarks on a captivating journey into the realm of waves and the electromagnetic spectrum, unveiling their fundamental principles and far-reaching applications.
This comprehensive resource delves into the nature of waves, their diverse classifications, and their fundamental properties. It meticulously examines the electromagnetic spectrum, unraveling the unique characteristics and applications of its constituent waves, ranging from radio waves to gamma rays.
Introduction to Waves
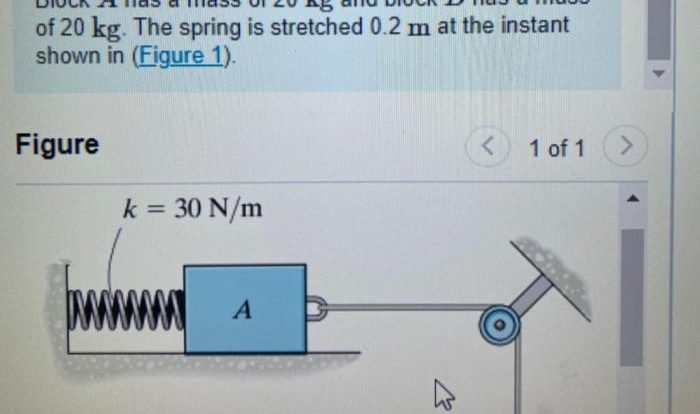
A wave is a disturbance that propagates through a medium, transferring energy without transporting matter. Waves are characterized by their wavelength, frequency, and amplitude.
There are two main types of waves: mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. Mechanical waves require a medium to propagate, such as sound waves in air or water waves in a liquid. Electromagnetic waves, on the other hand, do not require a medium and can travel through a vacuum, such as light waves or radio waves.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum, Waves & electromagnetic spectrum worksheet
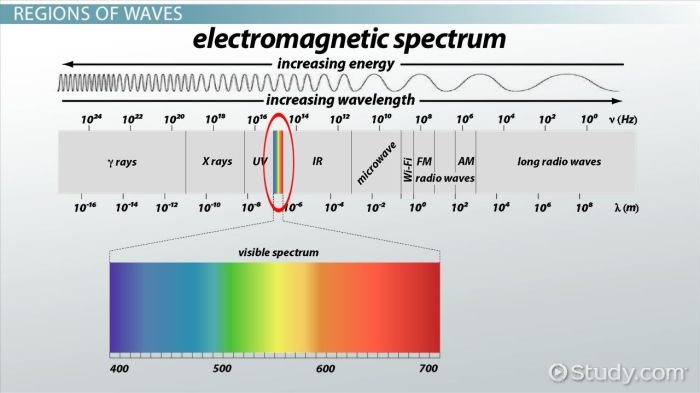
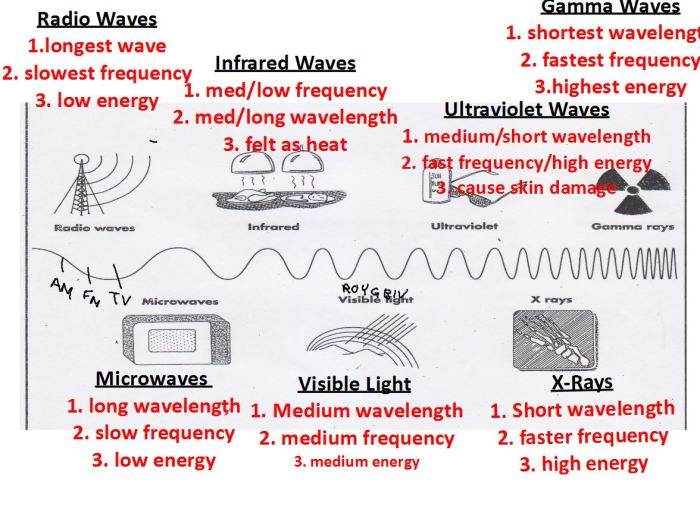
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. It is divided into seven regions, based on the wavelength and energy of the waves: radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies, while gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies. The visible light spectrum is the only part of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be detected by the human eye.
Interactions between Waves and Matter
When waves interact with matter, they can be reflected, refracted, or absorbed. Reflection is the bouncing back of a wave from a surface. Refraction is the bending of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. Absorption is the conversion of wave energy into other forms of energy, such as heat.
The interactions between waves and matter have many applications, such as lenses, mirrors, and antennas.
Applications of Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Waves and the electromagnetic spectrum have a wide range of applications in everyday life, including communication, transportation, and medicine.
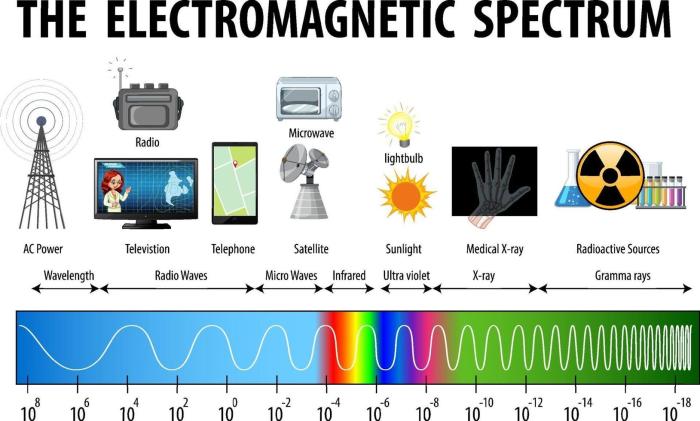
Radio waves are used for communication, such as in cell phones and televisions. Microwaves are used for cooking and heating. Infrared waves are used for night vision and thermal imaging. Visible light is used for seeing and photography. Ultraviolet waves are used for tanning and disinfection.
X-rays are used for medical imaging. Gamma rays are used for cancer treatment and sterilization.
Commonly Asked Questions: Waves & Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet
What is the difference between mechanical and electromagnetic waves?
Mechanical waves require a medium for propagation, while electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum.
How are waves used in communication?
Electromagnetic waves, particularly radio waves and microwaves, are widely employed in communication systems for transmitting information over long distances.
What are the applications of the electromagnetic spectrum in medicine?
The electromagnetic spectrum finds applications in medical imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans, enabling the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions.