A food worker finishes cleaning and sanitizing the kitchen, marking the completion of a crucial task in maintaining food safety and public health. This process involves adhering to strict regulations and standards, employing effective techniques, and monitoring practices to ensure a clean and hygienic kitchen environment.
Proper cleaning and sanitizing practices are essential in preventing foodborne illnesses, ensuring the safety of food products, and upholding the integrity of the food industry. This article delves into the step-by-step procedures, relevant regulations, and best practices involved in kitchen cleaning and sanitizing, emphasizing its significance for food safety and public health.
Kitchen Cleaning and Sanitizing Procedures
To ensure a clean and sanitary kitchen environment, it is essential to follow proper cleaning and sanitizing procedures. These procedures involve a series of steps designed to remove dirt, grime, and microorganisms from surfaces, equipment, and utensils.
Step-by-Step Cleaning and Sanitizing Procedures
- Pre-cleaning:Remove all food debris and visible dirt from surfaces using a damp cloth or sponge.
- Cleaning:Use a cleaning solution appropriate for the surface being cleaned (see Table 1) and apply it to the surface. Scrub the surface thoroughly using a clean cloth or sponge.
- Rinsing:Rinse the surface thoroughly with clean water to remove any remaining cleaning solution.
- Sanitizing:Apply a sanitizing solution to the surface according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Allow the solution to remain on the surface for the required contact time (see Table 1).
- Air Drying:Allow the surface to air dry completely before use.
Recommended Cleaning and Sanitizing Agents
| Surface/Equipment | Cleaning Agent | Concentration | Contact Time | Sanitizing Agent | Concentration | Contact Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food contact surfaces | Chlorine bleach | 100 ppm | 1 minute | Quaternary ammonium | 200 ppm | 30 seconds |
| Non-food contact surfaces | All-purpose cleaner | Follow manufacturer’s instructions | – | Alcohol-based sanitizer | 70% | 30 seconds |
| Equipment | Detergent solution | Follow manufacturer’s instructions | – | Chlorine bleach | 100 ppm | 1 minute |
| Utensils | Dishwashing detergent | Follow manufacturer’s instructions | – | Heat (171°F/77°C) | – | 15 seconds |
Food Safety Regulations and Standards
Kitchen cleaning and sanitizing practices are subject to various food safety regulations and standards. These regulations aim to prevent the spread of foodborne illnesses and ensure the safety of food products.
Key Requirements
- Temperature control:Maintain proper temperatures for food storage, cooking, and cooling to prevent bacterial growth.
- Cross-contamination prevention:Separate raw and cooked foods, use separate cutting boards and utensils, and store foods properly to prevent cross-contamination.
- Employee hygiene:Employees must maintain proper hygiene practices, including handwashing, wearing clean uniforms, and covering open wounds.
Relevant Regulations and Standards
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Food Code:Provides detailed guidelines for food safety practices, including kitchen cleaning and sanitizing.
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP):A preventive food safety system that identifies and controls potential hazards throughout the food production process.
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 22000:A family of standards that provides requirements for food safety management systems.
Importance of Kitchen Hygiene
Maintaining a clean and sanitized kitchen is essential for food safety and public health. Proper cleaning and sanitizing practices help prevent the spread of foodborne illnesses caused by harmful bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
Foodborne Illnesses
- Foodborne illnesses can range from mild to severe, causing symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
- Some foodborne illnesses, such as E. coli and Salmonella, can be life-threatening, especially for vulnerable populations like children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems.
Prevention, A food worker finishes cleaning and sanitizing the kitchen
Proper kitchen hygiene practices, including regular cleaning and sanitizing, help prevent foodborne illnesses by removing and killing microorganisms that can contaminate food.
Best Practices for Kitchen Cleaning and Sanitizing
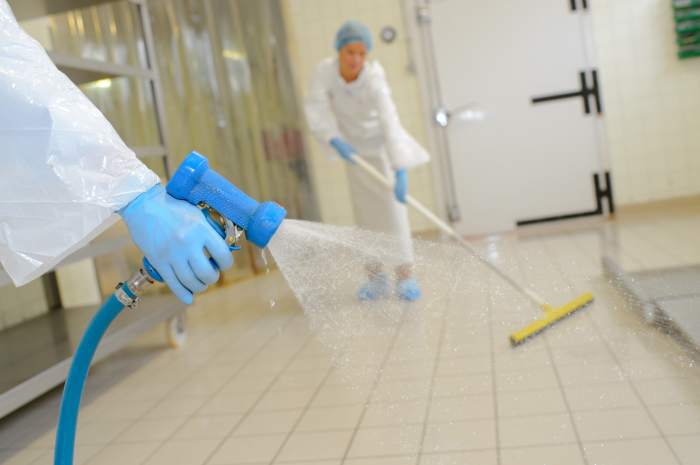

Effective kitchen cleaning and sanitizing require following best practices that ensure a high level of hygiene and food safety.
Frequency
- Clean and sanitize food contact surfaces after each use.
- Clean and sanitize non-food contact surfaces daily or as needed.
- Deep clean the kitchen, including equipment and storage areas, regularly.
Techniques
- Use the appropriate cleaning and sanitizing agents for different surfaces and equipment.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for use and contact times.
- Use clean cloths, sponges, and brushes, and replace them regularly.
Equipment Selection
- Use equipment designed for easy cleaning and sanitizing.
- Avoid using wooden or porous materials that can harbor bacteria.
- Consider using automated cleaning and sanitizing systems for large-scale kitchens.
Organization and Storage
- Keep the kitchen organized to prevent clutter and cross-contamination.
- Store food and equipment properly to prevent spoilage and contamination.
- Label all food and cleaning products clearly to avoid confusion.
Monitoring and Evaluation of Cleaning and Sanitizing Practices

Regular monitoring and evaluation are crucial to ensure the effectiveness of kitchen cleaning and sanitizing practices.
Methods
- Visual inspections:Regularly inspect surfaces, equipment, and utensils for cleanliness and signs of contamination.
- Microbial testing:Periodically test surfaces for the presence of microorganisms to verify the effectiveness of cleaning and sanitizing procedures.
- Employee observations:Monitor employee compliance with cleaning and sanitizing procedures through observation and training.
Corrective Actions
Based on monitoring results, take corrective actions as needed to address any deficiencies in cleaning and sanitizing practices. This may include retraining employees, adjusting cleaning schedules, or implementing new technologies.
Top FAQs: A Food Worker Finishes Cleaning And Sanitizing The Kitchen
What are the key steps involved in cleaning and sanitizing a kitchen?
Cleaning and sanitizing a kitchen involves removing dirt, food residue, and microorganisms from surfaces and equipment. It typically includes steps such as pre-cleaning, washing, rinsing, sanitizing, and air-drying.
What are the recommended cleaning and sanitizing agents for different surfaces?
The choice of cleaning and sanitizing agents depends on the surface being treated. Common agents include detergents, degreasers, and sanitizers approved for food contact surfaces.
How often should a kitchen be cleaned and sanitized?
The frequency of cleaning and sanitizing depends on the level of activity in the kitchen. High-traffic areas may require daily cleaning and sanitizing, while less frequently used areas may be cleaned and sanitized less often.
What are the consequences of improper kitchen cleaning and sanitizing?
Improper cleaning and sanitizing can lead to the accumulation of dirt, food residue, and microorganisms, increasing the risk of foodborne illnesses and compromising the safety of food products.