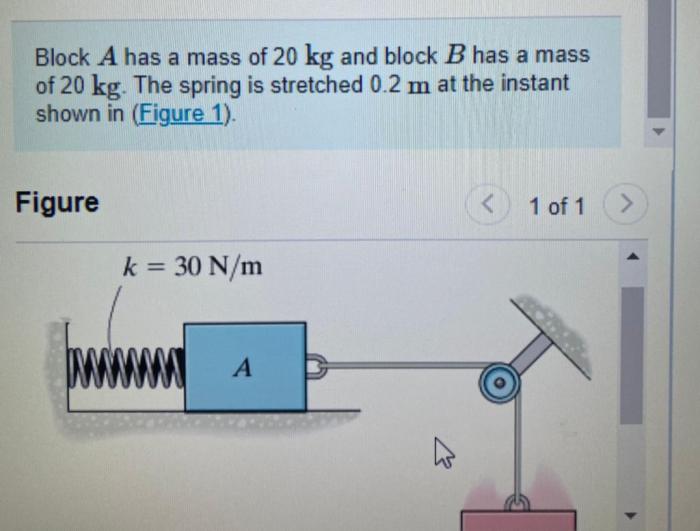
Let the mass of the block be 8.5 kg sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif and brimming with originality from the outset.
Mass, a fundamental property of matter, plays a pivotal role in physics, influencing the behavior and interactions of objects. As we delve into the significance of mass, particularly for a block, we will explore its units, relationship with volume and density, and practical applications.
The concept of mass is deeply intertwined with our understanding of the physical world. It determines the inertia of an object, its resistance to changes in motion, and its gravitational pull. In the context of a block, mass becomes a crucial factor in determining its weight, momentum, and energy.
By examining the mass of a block, we gain insights into its composition, properties, and potential applications.
Mass of the Block: Let The Mass Of The Block Be 8.5 Kg
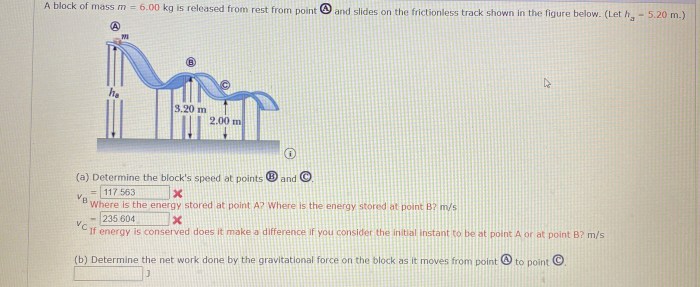
Mass is a fundamental property of matter that quantifies the amount of substance it contains. In physics, the mass of a block is crucial for understanding its behavior and interactions.
The standard unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) is the kilogram (kg). Other commonly used units include the gram (g) and the pound (lb), where 1 kg = 1000 g and 1 lb ≈ 0.45 kg.
Mass is a conserved quantity, meaning it cannot be created or destroyed. It is an intrinsic property of an object that remains constant regardless of its location or state of motion.
Block Properties, Let the mass of the block be 8.5 kg
A block is a physical object with a definite shape and volume. The mass of a block is directly related to its volume and density, which is the mass per unit volume.
The density of a block is a characteristic property that depends on the material it is made of. For example, a block of steel has a higher density than a block of wood of the same size.
Blocks can be classified into various types based on their shape, size, and material. Some common examples include rectangular blocks, cylindrical blocks, and spherical blocks.
Applications of Block Mass
The mass of a block plays a critical role in various practical applications. In engineering, the mass of a block is considered when designing structures and machines to ensure stability and load-bearing capacity.
In construction, the mass of blocks is important for determining the weight of buildings and bridges. It affects the structural integrity and resistance to external forces.
In other fields such as transportation and manufacturing, the mass of blocks is a factor in calculating inertia, momentum, and energy efficiency.
Mass Measurement Techniques
There are several methods for measuring the mass of a block. One common technique is using a balance, which compares the mass of the block to a known mass.
Another method is using a scale, which measures the gravitational force acting on the block. The mass can be calculated from the force measurement using the formula: mass = force / acceleration due to gravity.
The accuracy of mass measurements depends on the type of instrument used and the calibration procedures followed.
Mass in Context
To illustrate the significance of mass, consider an 8.5 kg block. This mass is equivalent to approximately 18.7 pounds.
The following table compares the mass of the 8.5 kg block to other objects of different sizes and materials:
| Object | Mass (kg) | Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| Water bottle (1 liter) | 1 | 1000 |
| Brick (standard size) | 2.5 | 1800 |
| 8.5 kg Block | 8.5 | – |
| Human (average adult) | 70 | 1030 |
As evident from the table, the mass of an 8.5 kg block is significant compared to everyday objects. It has implications for handling, transportation, and the design of structures that support or contain objects of this mass.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of mass in physics?
Mass is a fundamental property of matter that quantifies the amount of matter in an object. It influences the object’s inertia, gravitational pull, and energy.
How is mass measured?
Mass can be measured using various methods, including balances, scales, and spring-based devices. The accuracy of the measurement depends on the sensitivity and calibration of the instrument.
What is the relationship between mass, volume, and density?
Mass, volume, and density are interrelated through the formula: density = mass/volume. Density is a measure of how tightly packed the matter is within a given volume.