Forces and newton’s laws worksheet answer key – Unveiling the intricate world of forces and Newton’s laws, this worksheet answer key serves as a beacon of knowledge, guiding students through the fundamental principles that govern the motion of objects. With precision and clarity, it illuminates the concepts of force, unravels the complexities of Newton’s laws, and empowers learners to apply these principles to real-life scenarios.
Forces
Forces are interactions that can cause objects to change their motion. They can be either contact forces, which require physical contact between objects, or non-contact forces, which act over a distance.
There are four fundamental types of forces: gravitational force, electromagnetic force, strong nuclear force, and weak nuclear force. Gravitational force is the force that attracts objects with mass towards each other. Electromagnetic force is the force that acts between charged particles.
Strong nuclear force is the force that holds the nucleus of an atom together. Weak nuclear force is the force that is responsible for radioactive decay.
Forces can affect objects in a variety of ways. They can cause objects to accelerate, decelerate, or change direction. They can also cause objects to deform or break.
Newton’s Laws of Motion
Newton’s laws of motion are three fundamental laws that describe the relationship between forces and the motion of objects.
Newton’s First Law of Motion
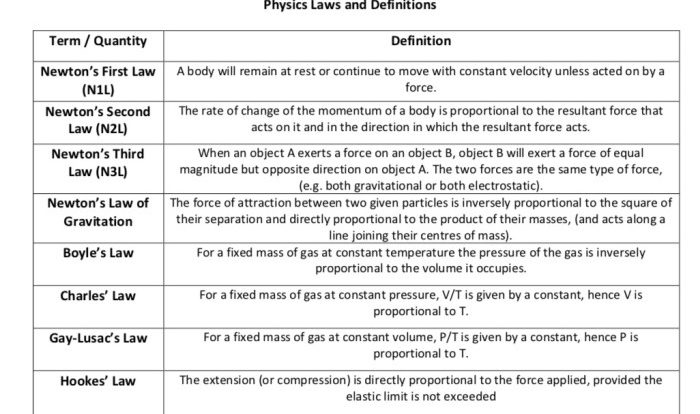
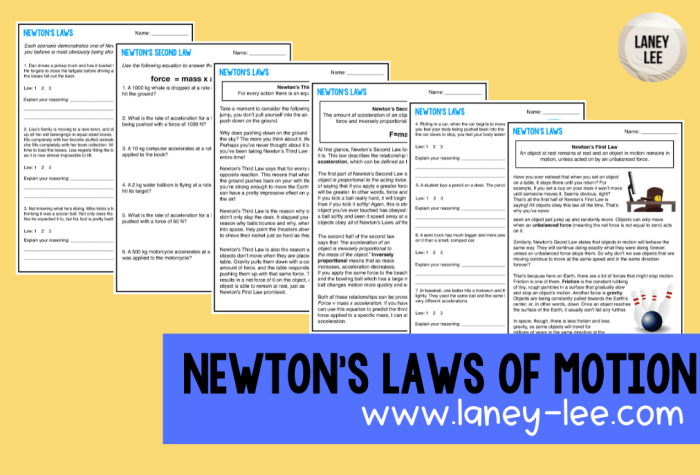
Newton’s first law of motion states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
Newton’s Second Law of Motion, Forces and newton’s laws worksheet answer key
Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Newton’s third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Worksheet Answer Key
| Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| What is the definition of force? | An interaction that can cause objects to change their motion. | |
| What are the four fundamental types of forces? | Gravitational force, electromagnetic force, strong nuclear force, and weak nuclear force. | |
| State Newton’s First Law of Motion. | An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. | |
| State Newton’s Second Law of Motion. | The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. | |
| State Newton’s Third Law of Motion. | For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. |
Examples and Applications
Forces and Newton’s laws are applied in a variety of real-life situations, including:
- The force of gravity keeps us on the ground.
- The force of friction allows us to walk and drive.
- The force of air resistance helps airplanes fly.
- Newton’s laws of motion are used to design and build machines.
Further Exploration
Top FAQs: Forces And Newton’s Laws Worksheet Answer Key
What is the concept of force?
Force is a physical quantity that describes an interaction between two objects, resulting in a change in their motion or shape.
What are the different types of forces?
There are various types of forces, including gravitational force, electromagnetic force, nuclear force, and frictional force.
How do forces affect objects?
Forces can cause objects to accelerate, decelerate, or change direction, depending on their magnitude and direction.