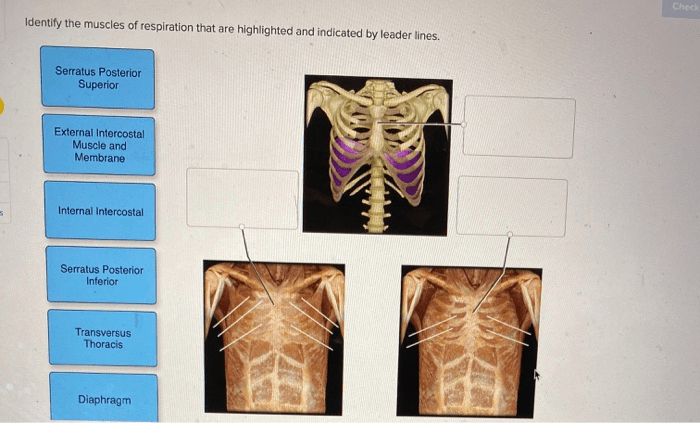
Identify the highlighted muscles of respiration. – The muscles of respiration play a crucial role in the life-sustaining process of breathing, enabling us to inhale and exhale with ease. This article delves into the intricacies of these muscles, exploring their functions, mechanisms, and clinical significance.
We will begin by identifying the primary muscles involved in respiration, examining their location, function, and innervation. This foundational understanding will lay the groundwork for comprehending the intricate mechanism of respiration, where we will explore the coordinated actions of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
Identify the Muscles of Respiration: Identify The Highlighted Muscles Of Respiration.
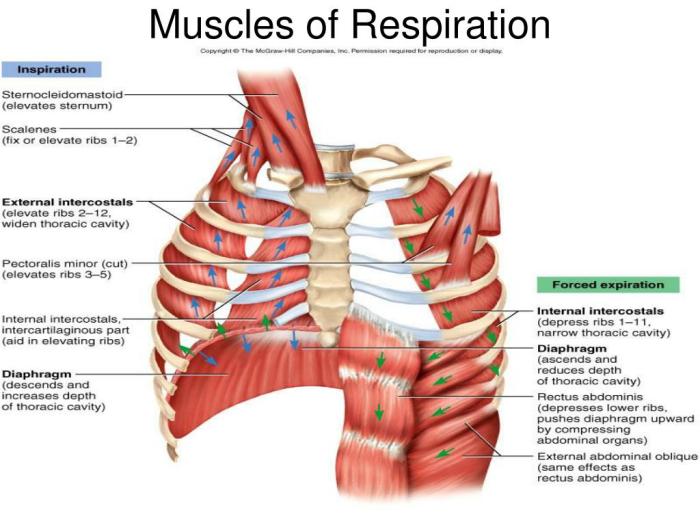
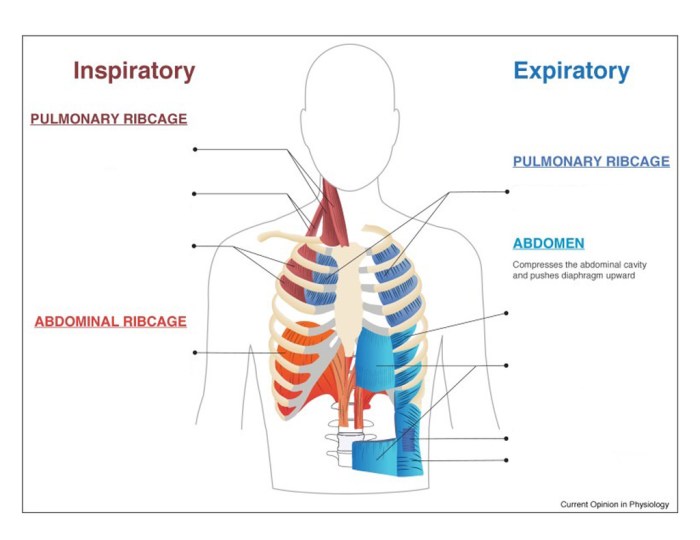
The muscles of respiration are responsible for the process of breathing, which involves the inhalation and exhalation of air. The primary muscles involved in inhalation are the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles, while the primary muscles involved in exhalation are the internal intercostal muscles and the abdominal muscles.
| Muscle Name | Location | Function | Innervation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diaphragm | Separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity | Contracts to increase the volume of the thoracic cavity, causing inhalation | Phrenic nerve |
| External intercostal muscles | Located between the ribs | Contract to lift the ribs, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity, causing inhalation | Intercostal nerves |
| Internal intercostal muscles | Located between the ribs, deep to the external intercostal muscles | Contract to lower the ribs, decreasing the volume of the thoracic cavity, causing exhalation | Intercostal nerves |
| Abdominal muscles | Located in the abdominal wall | Contract to compress the abdominal cavity, pushing the diaphragm upward and causing exhalation | Various nerves, including the phrenic nerve and the intercostal nerves |
FAQ
What is the primary function of the diaphragm?
The diaphragm is the primary muscle of respiration, responsible for separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. During inhalation, it contracts and flattens, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity and drawing air into the lungs.
How do the intercostal muscles contribute to respiration?
The intercostal muscles are located between the ribs and assist in both inhalation and exhalation. During inhalation, the external intercostal muscles contract, lifting the ribs and expanding the thoracic cavity. During exhalation, the internal intercostal muscles contract, pulling the ribs down and reducing the volume of the thoracic cavity.
What are some common respiratory disorders that affect muscle function?
Respiratory disorders such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia can weaken or impair the muscles of respiration, leading to difficulty breathing and other complications.