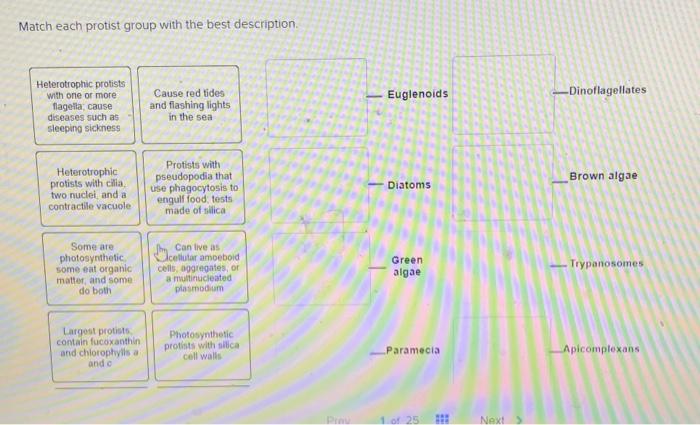
Match each protist group with the best description – Matching each protist group with the best description takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Protists, a diverse group of eukaryotic organisms, encompass a vast array of forms and functions. Understanding the unique characteristics of each protist group is crucial for unraveling their ecological roles, evolutionary relationships, and potential applications. This article embarks on a journey to match protist groups with their most appropriate descriptions, providing a comprehensive overview of their defining features and ecological significance.
Matching Protist Groups with Their Descriptions: Match Each Protist Group With The Best Description
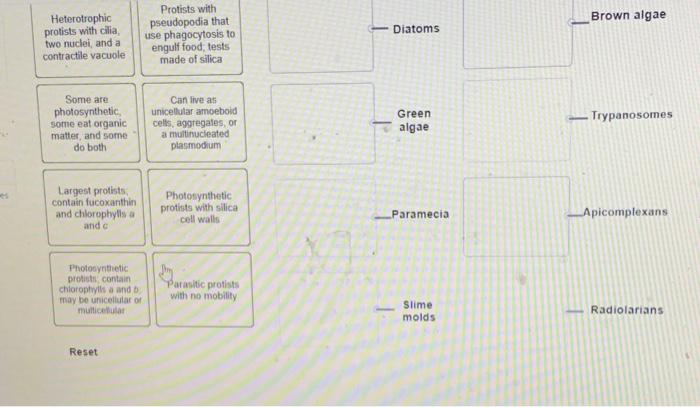
Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms that play crucial roles in various ecosystems. Accurately matching protist groups with their descriptions is essential for understanding their ecology, evolution, and potential applications. This article provides an overview of protist groups, their unique features, and a detailed analysis of how they align with specific descriptions.
Overview of Protist Groups, Match each protist group with the best description
Protists are characterized by their diverse morphology, motility, nutrition, and habitat preferences. They can be broadly categorized into:
- Protozoa:Animal-like protists that move using flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia. They are typically heterotrophic, consuming bacteria, algae, or other protists.
- Algae:Plant-like protists that contain chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis. They can be unicellular, colonial, or multicellular.
- Slime molds:Fungus-like protists that exhibit both unicellular and multicellular stages. They are typically saprophytic, feeding on decaying organic matter.
Matching Protist Groups to Descriptions
| Protist Group | Description |
|---|---|
| Protozoa | Motile, heterotrophic microorganisms |
| Algae | Photosynthetic, plant-like microorganisms |
| Slime molds | Saprophytic, fungus-like microorganisms |
Detailed Analysis of Matches
Protozoa:Protozoa are characterized by their motility, which is essential for capturing prey. Their heterotrophic nutrition involves ingesting other organisms, making them important consumers in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
Algae:Algae possess chlorophyll, enabling them to carry out photosynthesis and produce their own food. They form the base of many food chains and are vital primary producers in aquatic environments.
Slime molds:Slime molds are saprophytic, meaning they obtain nutrients from decaying organic matter. They play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and decomposition processes.
Significance and Applications
Understanding the descriptions of protist groups has practical implications in various fields:
- Ecology:Matching protists to their descriptions helps researchers identify and classify species, understand their ecological roles, and assess their impact on ecosystems.
- Biotechnology:Protists are valuable sources of bioactive compounds and enzymes with potential applications in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and industrial processes.
- Medicine:Some protists are pathogens that cause diseases, while others are used as model organisms for studying human health and disease.
FAQ
What are the main characteristics used to distinguish protist groups?
Protist groups are primarily distinguished based on their motility, nutrition, and habitat. Motility refers to their ability to move, while nutrition encompasses their mode of obtaining food (autotrophic or heterotrophic). Habitat describes the specific environments where they are found.
Why is it important to accurately match protist groups with their descriptions?
Accurate matching is essential for understanding the diversity of protists, their ecological roles, and their potential applications. It allows researchers to identify and classify protists, study their interactions with other organisms, and explore their potential uses in biotechnology and medicine.
What are some examples of protist groups and their defining characteristics?
Protozoa are heterotrophic protists that move using flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia. Algae are autotrophic protists that use photosynthesis to produce food. Slime molds are heterotrophic protists that form mobile colonies and feed on bacteria and other microorganisms.