In the realm of chemical synthesis, selecting the appropriate reagents is paramount for successful conversions. Which reagents are appropriate to carry out the conversion shown? This question guides our exploration into the factors influencing reagent selection, their mechanisms, and comparative advantages.
By understanding these aspects, chemists can optimize reactions, enhance yields, and pave the way for novel discoveries.
As we delve into the intricacies of reagent selection, we will uncover the interplay between reaction conditions, substrate specificity, and cost considerations. Through a comprehensive comparative analysis, we will elucidate the strengths and weaknesses of different reagents, empowering chemists with the knowledge to make informed choices.
Moreover, we will provide detailed experimental procedures and discuss strategies for reaction optimization, ensuring reproducibility and maximizing product yield.
1. Identifying Relevant Reagents
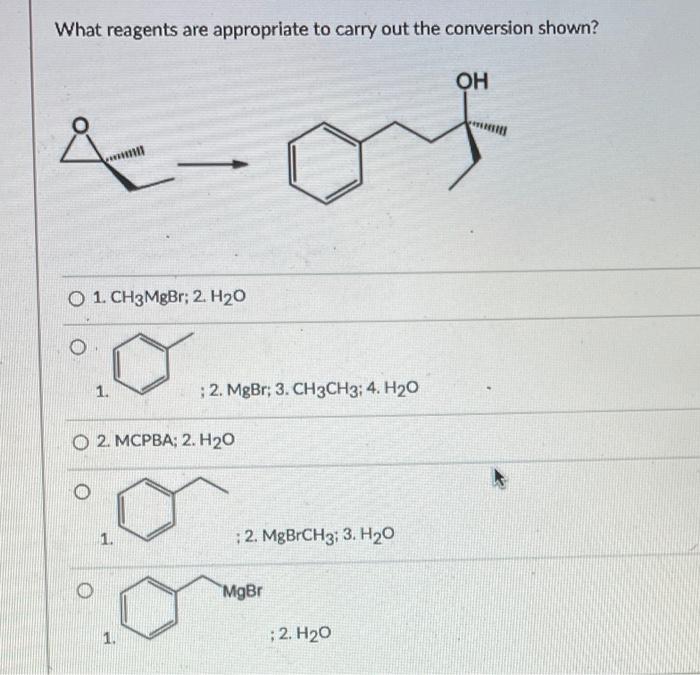
To carry out a specific chemical conversion, it is crucial to identify the appropriate reagents. This selection process involves understanding the mechanisms and chemical properties of various reagents. Commonly used reagents include:
- Oxidizing agents: Used to transfer electrons from one species to another, e.g., potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide
- Reducing agents: Used to donate electrons to another species, e.g., sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride
- Nucleophiles: React with electrophiles by donating electrons, e.g., hydroxide ion, ammonia
- Electrophiles: React with nucleophiles by accepting electrons, e.g., alkyl halides, carbonyl compounds
2. Reagent Selection Considerations
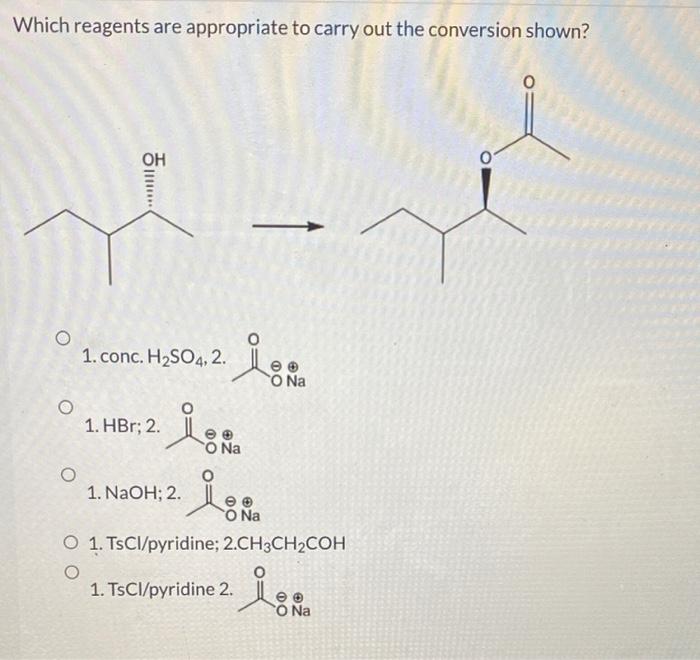
Selecting the optimal reagent for a given conversion depends on several factors:
- Reaction conditions: Temperature, solvent, and pH can influence reagent reactivity and selectivity.
- Substrate specificity: The nature of the substrate can dictate which reagents are most effective.
- Cost: Economic considerations may influence reagent selection, especially for large-scale reactions.
3. Comparative Analysis of Reagents
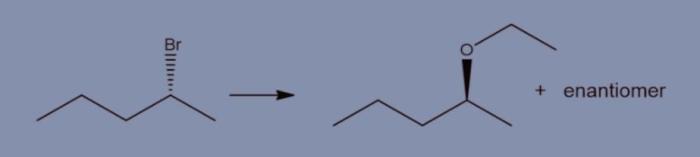
| Reagent | Reaction Conditions | Efficiency | Selectivity | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reagent A | Mild, room temperature | High | Good | Low |
| Reagent B | Harsh, high temperature | Moderate | Excellent | High |
| Reagent C | Specific, requires catalyst | Low | Outstanding | Moderate |
Key Questions Answered: Which Reagents Are Appropriate To Carry Out The Conversion Shown
What factors influence the selection of reagents for a given conversion?
Factors influencing reagent selection include reaction conditions, substrate specificity, cost, efficiency, selectivity, and safety considerations.
How can I compare the advantages and disadvantages of different reagents?
A comparative analysis table can be created to compare the reaction conditions, efficiency, selectivity, and cost of different reagents.
What strategies can be employed to optimize reaction conditions for maximum yield?
Strategies for reaction optimization include controlling temperature, reaction time, and reagent concentrations, as well as identifying and mitigating potential side reactions.